 10 March 2021
10 March 2021
5G and Fiber Optic Infrastructure
5G and Fiber Optic Infrastructure
The revolutionary (5G) fifth generation of mobile networks, compared to the current 4G/3G networks, provides low latency, higher bandwidth, superior reliability and the ability to connect more devices in a smaller area.
With 5G Technology, speeds can reach up to 10 times faster than 4G, and delays in packet transmission are reduced by at least 20 times to 1ms. In addition, the increased density of network-connected devices will allow up to 1 million devices in one square kilometer to connect to a 5G network.
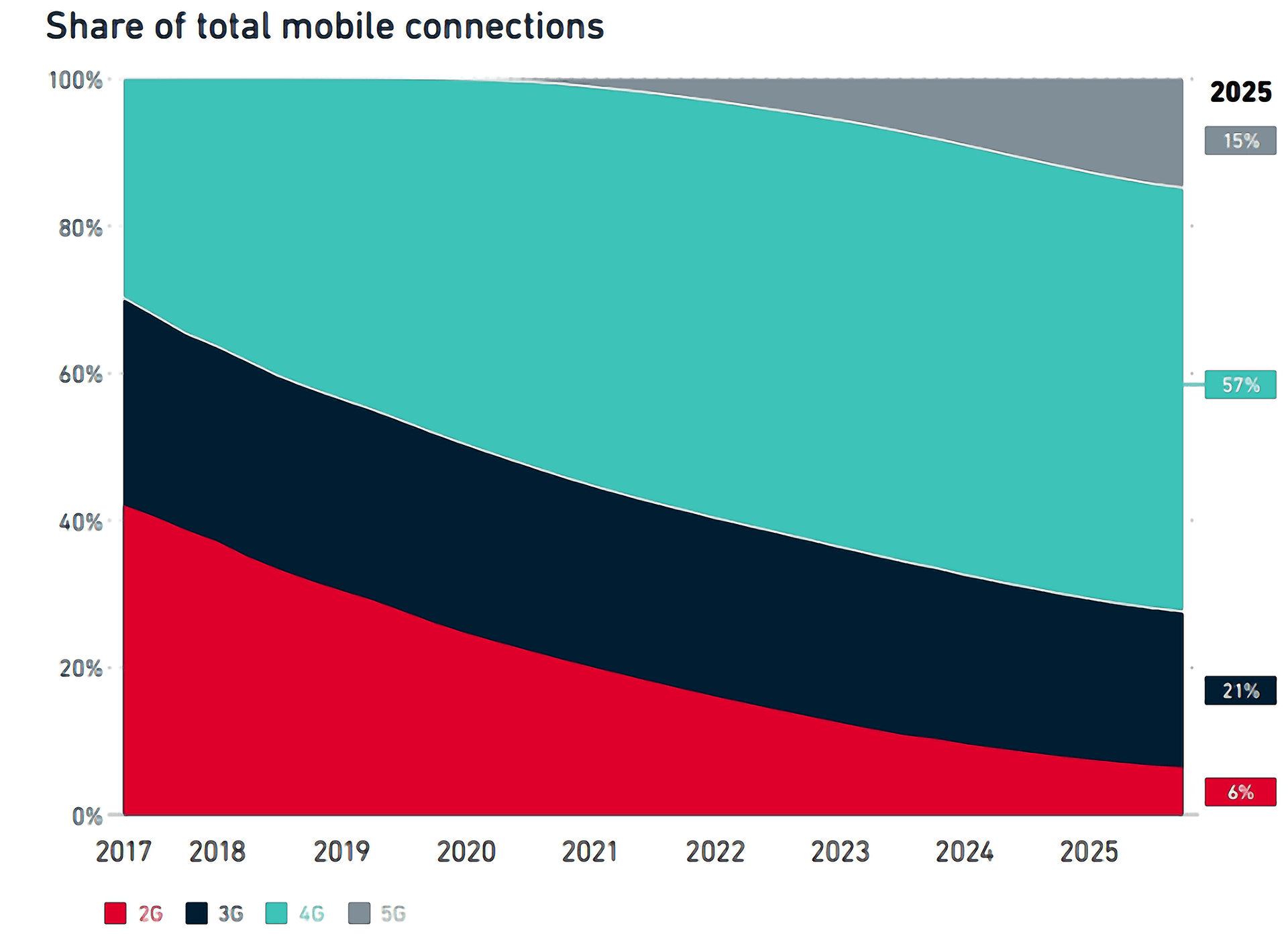
25 operators worldwide are expected to offer 5G service in 2019 and this number is expected to double in 2020. According to the “The Mobile Economy 2019” report by the World GSM Association GSMA, 5G technology is expected to run 15% of global mobile connections in 2025.
Turkey, like many other countries, has started its 5G test run; which is done by ICTA licensed operators and will provide the 5G technology service in 2020. 5G Technology requires a lot of testing and analysis in order to have a solid and stable service. It is not enough to replace old antennas in existing cellular base stations with new ones. A completely new infrastructure must be designed, installed and commissioned and all these processes have further difficulties and challenges themselves.
The installation of the next generation mobile network 5G will not take place in an instant. As illustrated in the chart below, the 4G (LTE / LTE-A) technology will still have the largest 57% share in 2025.
The 5G Network Architecture requires a lot of changes to be considered for the end-to-end installation of a network, which can be listed as the following:
1. More Antennas/Base Stations
The range of “macro cell” mobile base stations available in 4G networks is approximately 25 km² for each station. New mobile base stations with 5G technology will not be able to cover such wide coverage area. Instead, 5G requires multiple smaller miniature base stations or antennas, with narrower coverage area, called “small cell”, “femtocell” or “picocells”. In 5G networks, an area as small as 3 km² would require the installation of up to 60 “small cell” mobile base station. Accordingly, the number of antennas required will be increased up to 600 times the number of station antennas used in 4G networks.
All these antennas and small base stations are connected to the to the FTTA fiber infrastructure using high bandwidth 5G distributed units, which can be called 5G DU.
2. Placement of Antenna / Base Stations
In addition to existing roof antennas and tower antennas, 5G networks installation will require additional low level antennas to provide the best coverage. For this purpose, structures such as electricity poles, street lights, traffic lights, bus stops and other building surfaces will be used for antenna installation, and due to their high operating frequency, 5G antennas will also need to be installed inside buildings to ensure best results.
3. Fiber Optic Cabling Infrastructure
As shown in the illustration below the main backbone in a 5G network involves many elements extensively installed throughout the network, such as: NGC (Next Generation Core), MEC (Multi-Access Edge Computing) Data Centers and AAS (Active Antenna Systems) with 5G NR support.
The infrastructure used for 5G Active Antenna System (AAS), which is the access (RAN-Fronthaul) network of mobile network, needs to feature multiple technologies used together, such as: NGPON, CWDM, DWDM, eCPRI, RATIO etc. All these technologies require a compatible optical fiber infrastructure.
Due to the high bandwidth and speed requirements of the 5G mobile network, fiber optic cable infrastructure is required be installed up to the antenna.
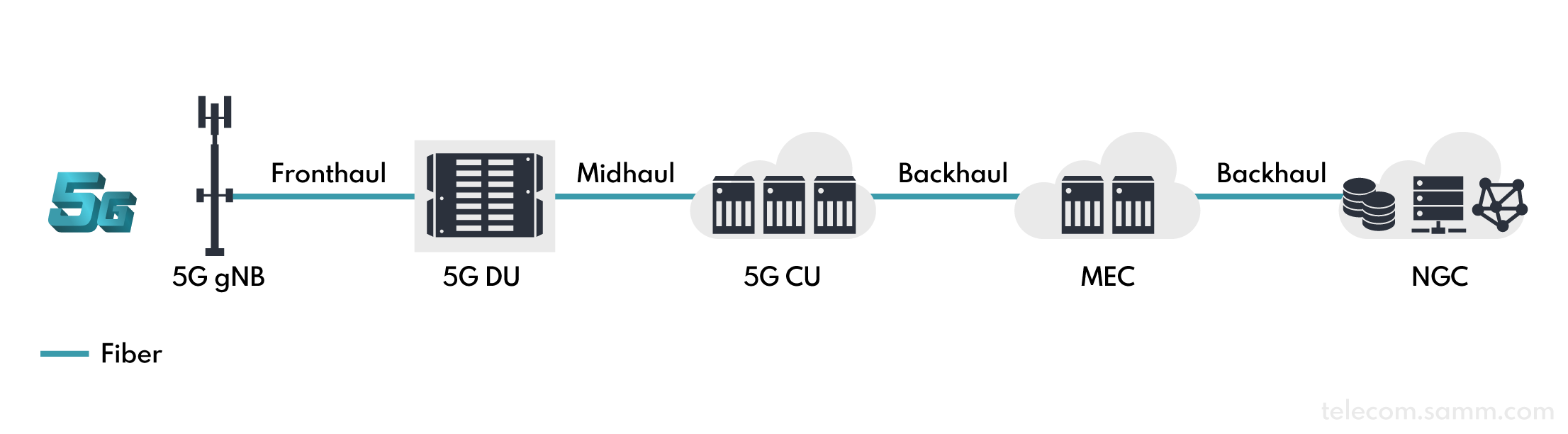
Therefore, in addition to increasing the main backbone fiber capacity, it is necessary to install the 5G mobile network as close as possible to the antennas of the fiber infrastructure and to install a new fiber optic cable infrastructure where the capacity is insufficient for more antennas.
4. Edge Computing (Edge Data Processing - Edge Data Centers)
As we mentioned at the beginning of the article, the two most important features of 5G Technology are its low latency and the ability to connect to millions of devices per square kilometer. Therefore, data processing needs to be close to mobile devices, so that data can be processed and transmitted to mobile devices without delay. In order to achieve this, MEC (Multi-Access Edge Computing) Data Centers should be installed where the antennas are most concentrated to support the low latency of the 5G mobile network infrastructure.
5. Investment and Operation Costs
The basic investment costs of the 5G Network are antennas, fiber optic cable infrastructure, electricity / energy infrastructure, installation / commissioning and data centers (edge computing). According to a report issued by Deloitte consulting firm, the amount of investment required to be made to fiber infrastructure in the next 6 years to meet the infrastructure need of 5G in the USA is between 130-150 billion dollars.
After the installation is completed, fiber optic infrastructure, maintenance and repair of active devices, power consumption of antennas, antenna rental fees and more costs are very serious operational costs in order to keep a 5G network up and running.
In addition, excavation is required for fiber infrastructure especially in city centers, and local authorities and municipalities need to obtain excavation permissions for fiber optic cable deployment operations. In order to use the resources correctly and efficiently, especially in our country, it is important to use the common infrastructure of the mobile networks.
We, as Samm Technology, locally develop the fiber optic cables and data center structural cabling solutions required for 5G mobile network infrastructures, and we will continue our efforts to produce low costs locally produced 5G infrastructure solutions with international quality standards.



About Samm Teknoloji
Fiber Optic Cable Manufacturer
Being a Turkish fiber optic cable manufacturer and an efficient supplier for Europe, Asia and America, SAMM Teknoloji joined the global market with very high potential. SAMM designs and manufactures a wide variety of fiber optic cable types optimized for fixed or mobile networks that can be used in indoor and outdoor environments. SAMM offers reliable, cost-effective optical products to meet the needs of customers with innovative products developed and tested in accordance with international standards.
Fiber Optic Assemblies Producer
As a fiber optic cable assemblies producer and supplier in Turkey and an optical assemblies supplier for Europe and Asia, Samm Teknoloji has been providing high-quality and reliable fiber optic cable assemblies since 2006. Due to our fully equipped production facilities, laboratories and long-term expertise in fiber optics, we are able to produce a first class fiber optic assemblies portfolio that ensure the highest level reliability. Therefore, one of the main priority is the ongoing expansion and advancement of the manufacturing capabilities.
Data Center Solutions Producer
As a Turkish producer of future-ready fiber optic data center equipment, SAMM Teknoloji produces UHD ultra high density MTP/MPO panels and cassettes, modular panels and cabling raceways. SAMM Teknoloji has also kept pace with the accelerating spread of Cloud Computing, which has increased the need for mega Data Centers. SAMM provides Data Center solutions and products that suit all structures with high data storage density, data traffic and data security.

