 23 March 2021
23 March 2021
Fiber Optic Cables Construction
There are several types of fiber optic cables, and they are differentiated according many construction properties like the core, buffer, fiber count, cable arrangement, sub units, filling, strength member, and outer jacket. Mixing all these properties, with each having its own derivative options, results in a large variety of fiber optical cables that can be used for different applications. In this article, we are explaining these differences and the main properties of each element of fiber cables' construction.
| Fiber Core and Cladding | Single Mode | Multi-mode |
|---|---|---|
| Fibers Count | Simplex | Duplex or Multiple |
| Cable Arrangement | Tight Buffer | Loose Tube |
| Sub Units | Cord Cable | Breakout Cable |
| Cable Filling | Gel-free | Gel-filled |
| Strength Member | Aramid Yarn | Glass Yarn |
| Cable Coating Jacket | Indoor Safe | Outdoor Resistant |
1- Fiber Core and Cladding
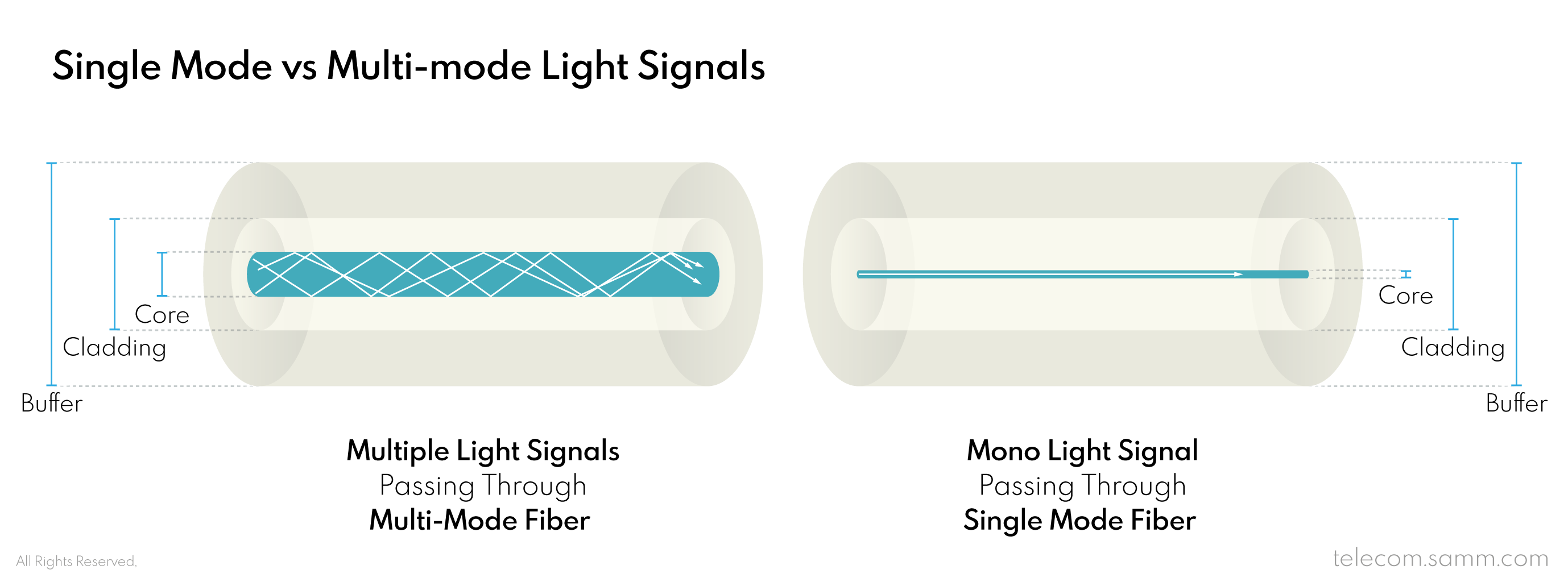
The diameter of the inner “Core” of a fiber strand defines the main usage of a fiber cable. A fiber with a 9µm (9 micrometer) diameter core allows only one single light pulse to pass through it at a time, thus it is called single mode fiber. On the other hand, a fiber with a 62.5µm or 50µm core diameter, allows for multiple pulses of light to refract and pass through it; and this type is called multi-mode fiber. Single mode fibers have a longer range but only transfer one signal; a single mode fiber can transfer one light signal up to 5 kilometers. Oppositely, multi-mode fibers can transfer several signals at the same time but to a shorter range; a multi-mode fiber can transfer multiple light signals up to 550 meters.
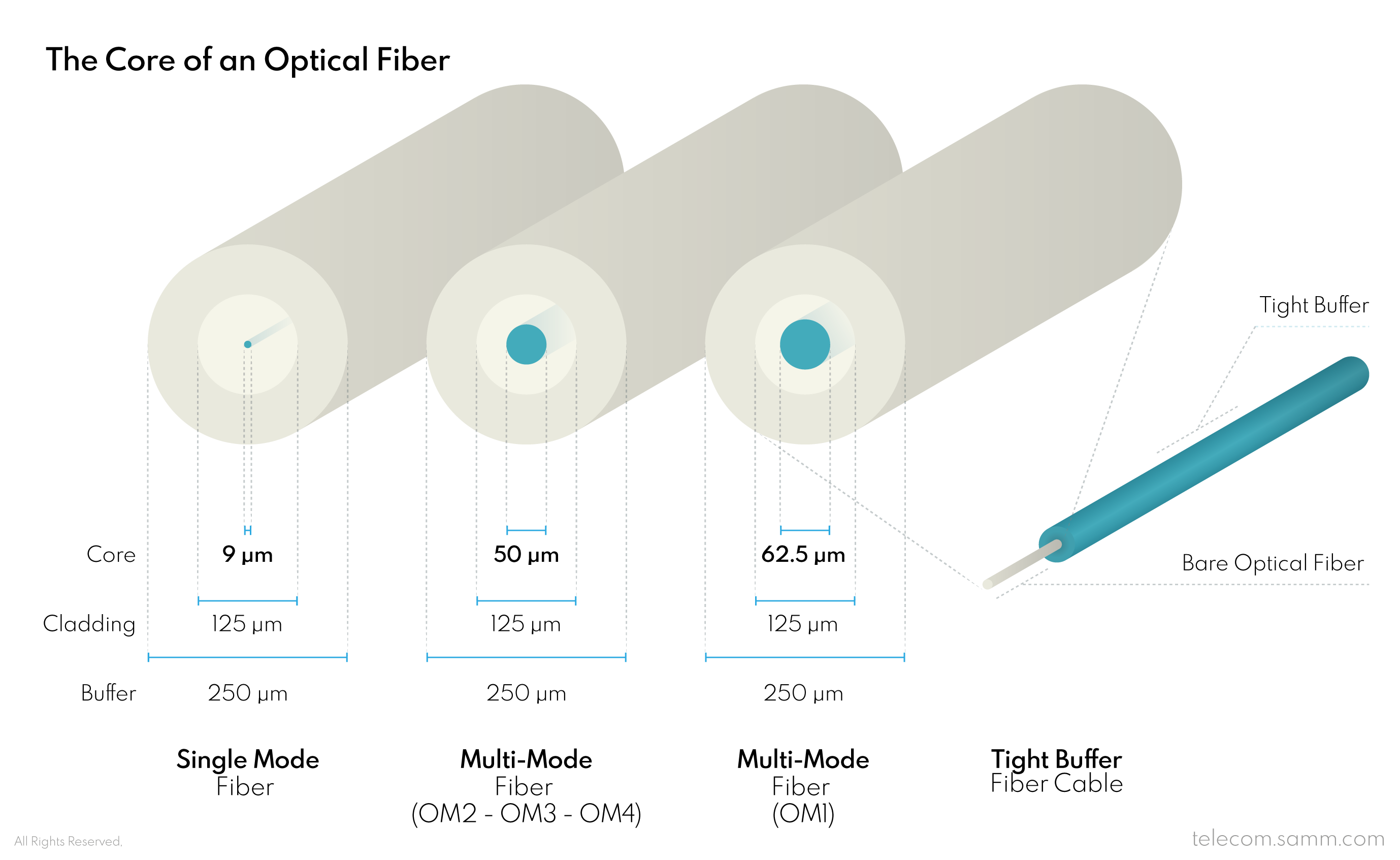
Whether the fiber core is the single or the multi type, both types of cores have a “Cladding” layer (up to a fixed 125µm diameter) that sticks perfectly to the core in order to provide the ultimate level refraction. There is also the “Buffer” layer, which is the first and direct protection layer that tightly holds the fiber cladding layer and core within it and also has a fixed diameter of 250µm. These three elements; Core, Cladding and Buffer; form a bare fiber strand that is the basis of all fiber optic cables.
2- Fibers Count
The count of fibers in a cable determines the count of channels of communication it can carry at the same time. Practically, a single fiber can only transfer in one direction at a time. Which means, in order for two optical transceivers to communicate with each other more quickly, they both need to be sending and receiving at the same time using two fibers as two channels of communication. Appropriately, there are three types of fiber cables according to fibers count: Simplex cables have one fiber and they are usually used for single sided data streaming, Duplex cables have two fibers and they are used mainly used in network distribution, and Multi-fiber cables have several fibers and they are used in network infrastructure and data centers. In Multi-Fiber cables, the buffer layer of fibers is made in distinctive colours to differentiate the number of each fiber in a groups of 12 or 24 fibers, the they are called colour-coded fibers.
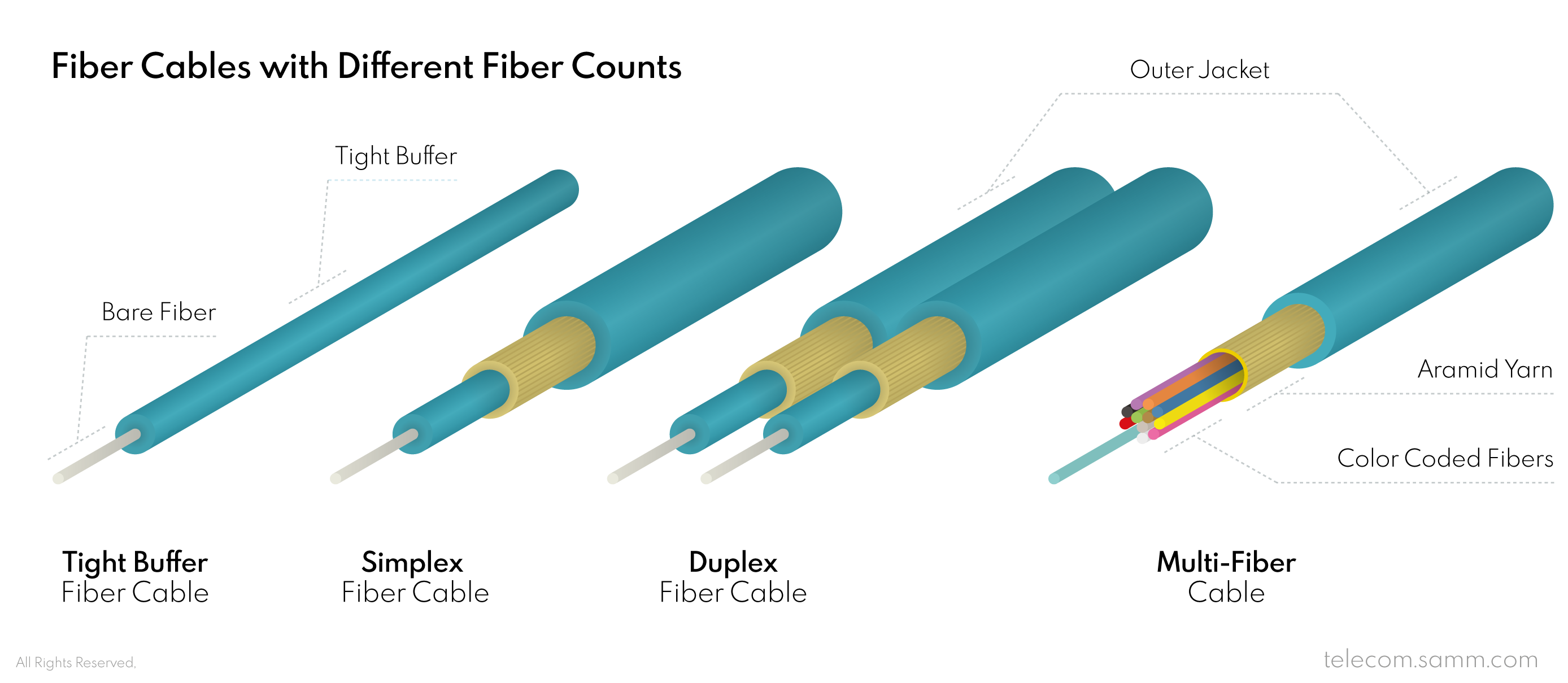
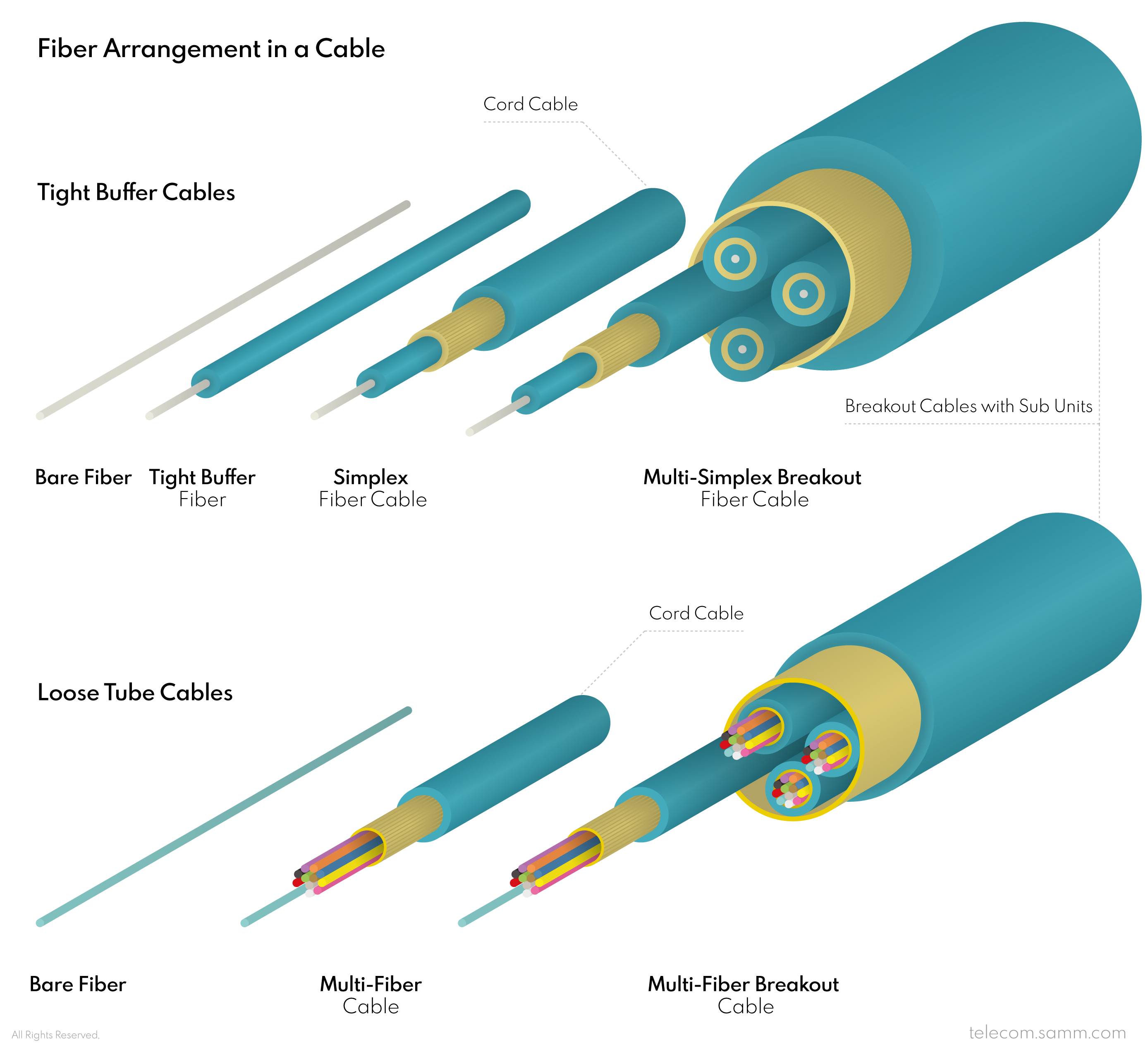
3- Cable Arrangement
Bare fiber strands are gathered together in cables in two methods. In the first method, each fiber has its own “Tight Buffer”, which is protective layer tightly holds the fiber within it and it is a rather sturdier, and more resistant to bending, which might cause a loss in signal. The Tight Buffer layer is usually 0.9mm in diameter and it helps in making the fiber easier to handle and is easier to break out at any point along the cable (when it has its own jacket) and be used as a single cable on its own. On the other hand, in cables that have so many fibers in them it is also an option to keep the fiber strands loose and packed together in a central tube that provides protection for all of them at once. This kind of cables is called “Loose Tube” cables, and they are good for gathering a large number of fiber lines in a relatively thin cables, which would have been very thick in diameter if each fiber had its own tight buffer. Tight Buffer are more practical for termination and they can be used in indoor and outdoor applications. To the contrary, Loose Tube Cables are usually used in outdoor applications because they are not as easy to terminate but they provide more protection for fiber against physical impacts.
4- Sub Units
When a Tight Buffer cable has more than two tight buffer fibers gathered as units, and each fiber unit has its own jacket and can be separated as a cable, it is called a “Breakout” cable. Differently, if a cable has fibers that do not have separated jackets and each one cannot be used as cable on its own, it is called a Cord cable or a Distribution cable. Breakout cables are usually used for on premises networks were a fiber cable has to be branched into multiple cables for different zones. Cord cables are used to connect from one point to another, whether they have few fibers and are used within buildings or they have large numbers of fibers and are used in broadband FTTX network infrastructure.
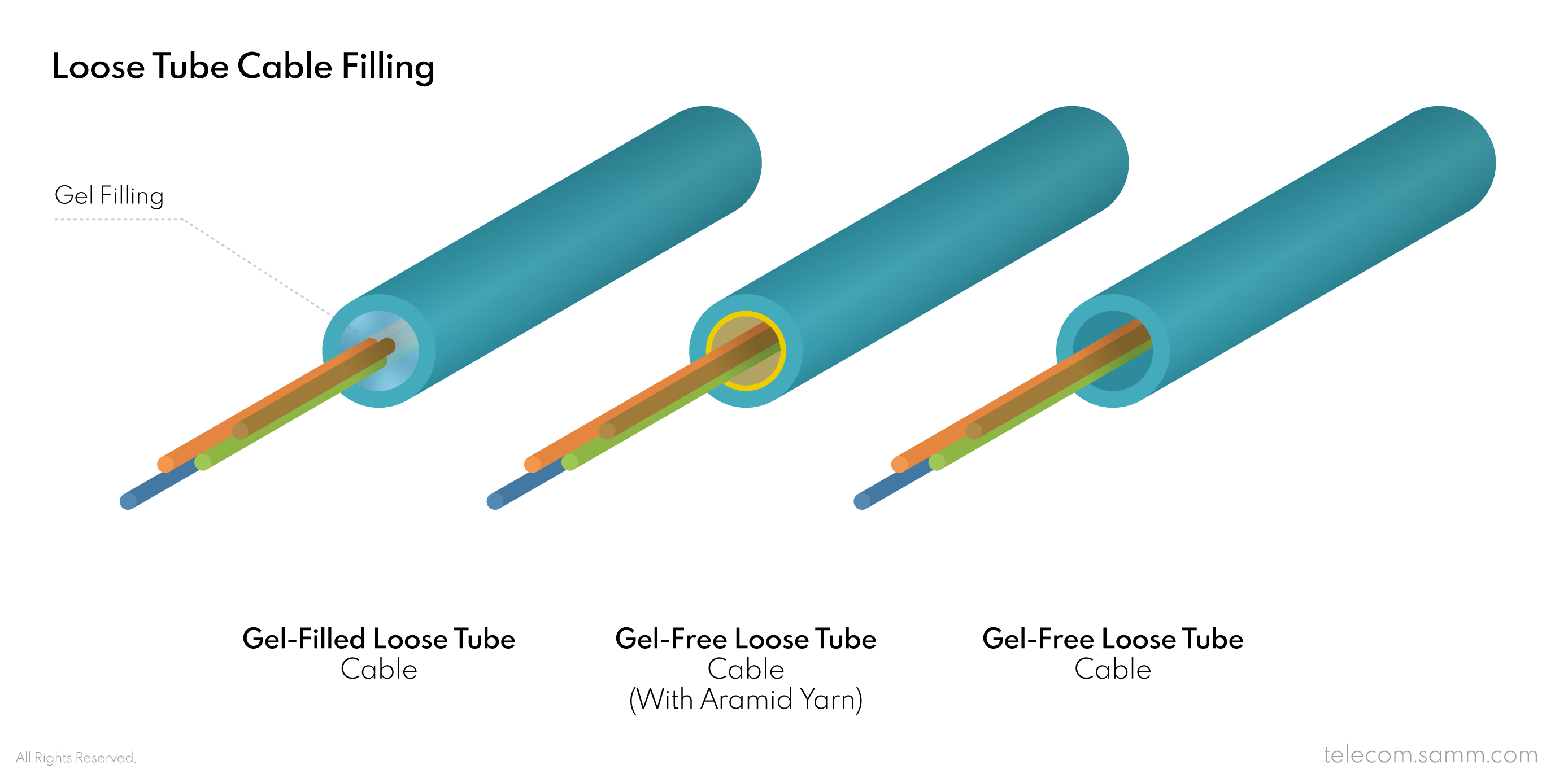
5- Fiber Cable Filling
There are two types of multi-fiber cables in case of filling, gel-free cables and gel-filled cables. In outdoor application, the central loose tube cables can be gel filled in order to provide more protection against moisture and physical impacts. Otherwise, cables that are kept dry, not filled with gel, are more suitable for indoor applications, which require safer materials in the mean of less fire propagation and more non-toxic human health friendly materials.
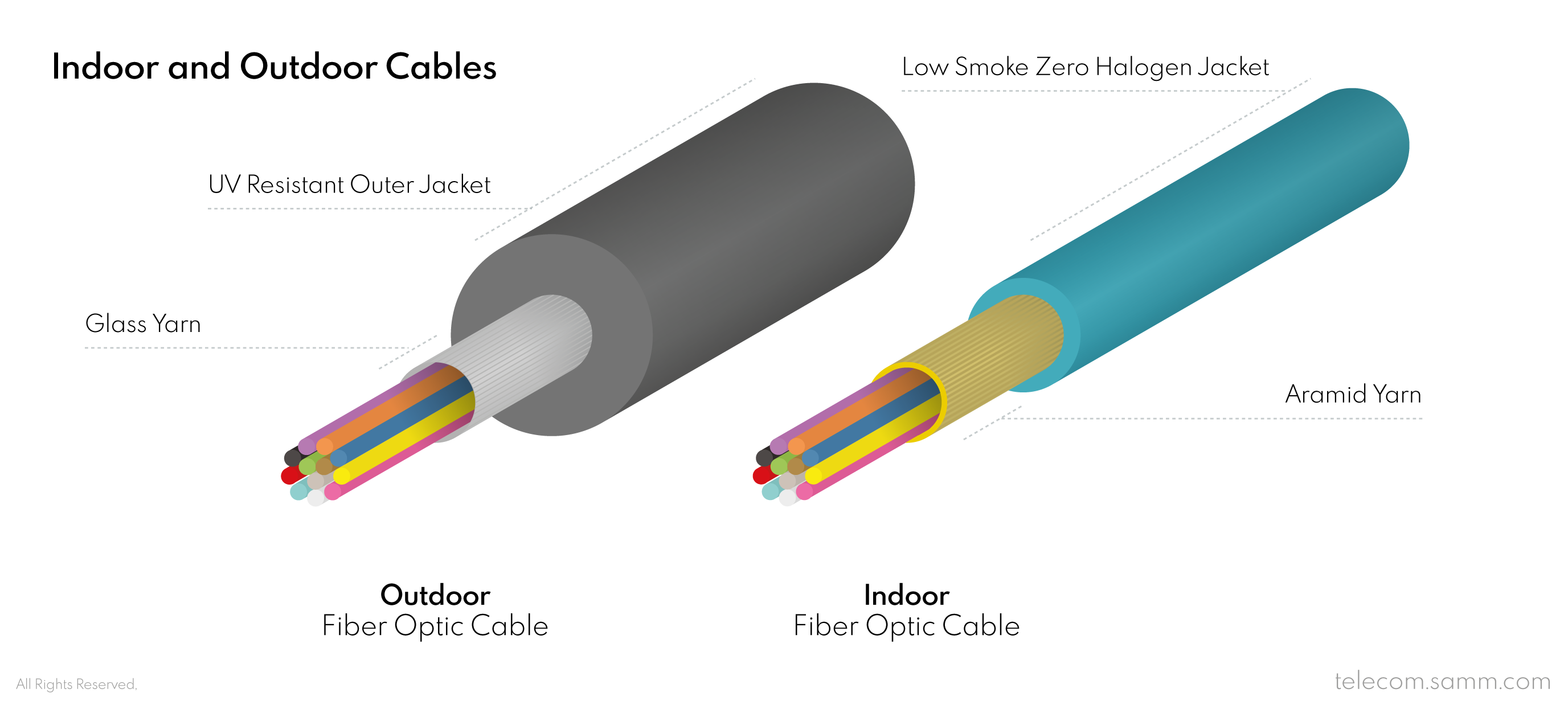
6- Strength Member
The strength member of a fiber cable is the layer that provides resistance against physical pulling or crush impacts and it is usually made of Aramid yarn or Glass yarn. Aramid yarn is a synthetic yarn that provides great strength and high temperature resistance. In indoor applications, aramid yarn is preferable for protecting the cable while being safer if cut or set on fire. On the other hand, not only does Glass yarn provide similar physical strength and heat protection but also it is sharp and edgy if broken, which makes it difficult for rodents to chew through the fiber cable in outdoor applications.
7- Cable Coating Jacket
Protecting the fiber cable is the main purpose of coating jackets, yet they usually differ according to the application area, whether it is indoor or outdoor. Indoor cables are meant not to be harmful in case of a fire. They usually have coating jackets that have a low smoke generation rate and are free of halogen materials; such as fluorine, chlorine, bromine and iodine; which produce toxic gasses if set on fire. Outdoor cables, on the contrary, have coating jackets that are made to protect the cables itself and they are made from materials that are resistant to the ambient environment, moisture, temperature shifts, impacts and ultra violet rays coming from the sun.
Finally, network infrastructure, which has fiber optic cables as its core element is constantly changing and improving. Thanks to research and development, there can be more and new properties and improvements in fiber optic cables' construction, and we will try to provide more info about them when they are presented.
For a closer look at fiber optic cables, you can check this category page, and do not hesitate to email us for more info on telecom@samm.com.



About Samm Teknoloji
Fiber Optic Cable Manufacturer
Being a Turkish fiber optic cable manufacturer and an efficient supplier for Europe, Asia and America, SAMM Teknoloji joined the global market with very high potential. SAMM designs and manufactures a wide variety of fiber optic cable types optimized for fixed or mobile networks that can be used in indoor and outdoor environments. SAMM offers reliable, cost-effective optical products to meet the needs of customers with innovative products developed and tested in accordance with international standards.
Fiber Optic Assemblies Producer
As a fiber optic cable assemblies producer and supplier in Turkey and an optical assemblies supplier for Europe and Asia, Samm Teknoloji has been providing high-quality and reliable fiber optic cable assemblies since 2006. Due to our fully equipped production facilities, laboratories and long-term expertise in fiber optics, we are able to produce a first class fiber optic assemblies portfolio that ensure the highest level reliability. Therefore, one of the main priority is the ongoing expansion and advancement of the manufacturing capabilities.
Data Center Solutions Producer
As a Turkish producer of future-ready fiber optic data center equipment, SAMM Teknoloji produces UHD ultra high density MTP/MPO panels and cassettes, modular panels and cabling raceways. SAMM Teknoloji has also kept pace with the accelerating spread of Cloud Computing, which has increased the need for mega Data Centers. SAMM provides Data Center solutions and products that suit all structures with high data storage density, data traffic and data security.

